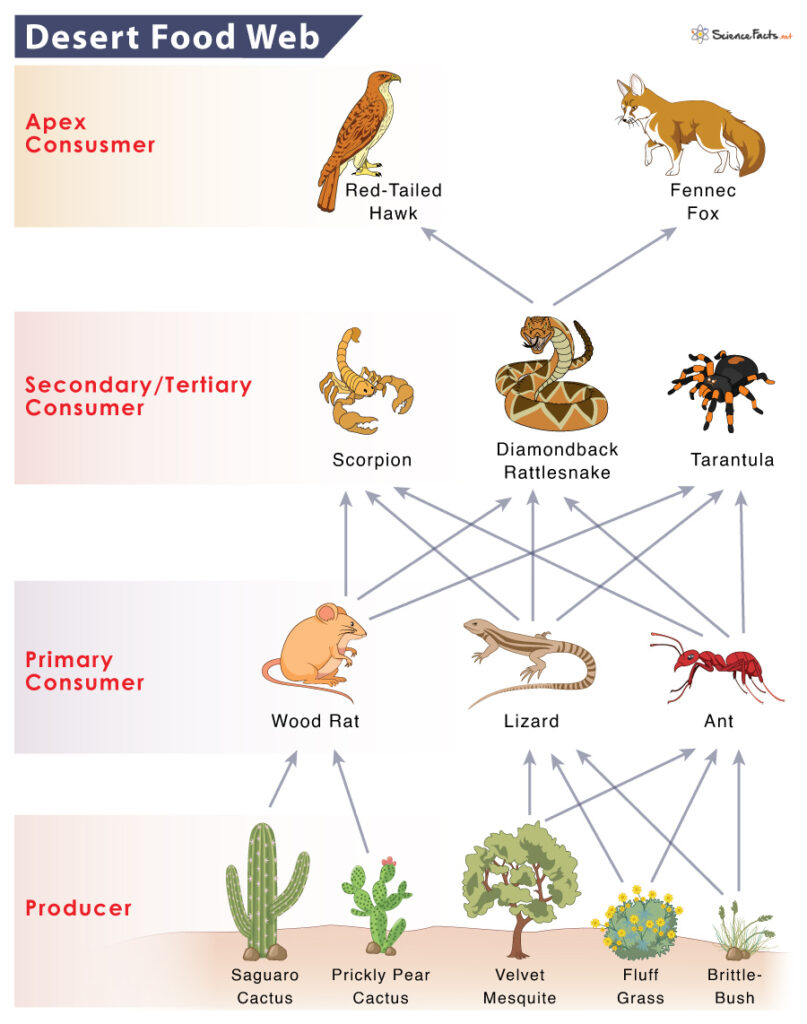
Is competition for resources truly the cornerstone of survival in ecosystems? A bold assertion suggests that without such competition, the balance of nature would collapse. The intricate web of life relies heavily on organisms vying for essential elements like food, water, and space. This concept extends beyond natural ecosystems into human-engineered environments where service animals and individuals with specific needs must coexist. Understanding these dynamics becomes crucial when addressing regulatory frameworks such as those provided by the ADA.
When considering scenarios involving service animals under ADA regulations, one must delve into the complexities of shared spaces. For instance, when a person allergic to dog dander encounters someone requiring a service animal within the same room or facility, the situation demands careful navigation. According to ADA guidelines, service animals are permitted access to areas where public accommodation is offered, including self-service food lines. Thus, while balancing individual rights, institutions must ensure compliance with legal standards ensuring equal access and safety for all parties involved.
| Personal Information | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | John Doe |
| Date of Birth | 1st January 1980 |
| Place of Birth | London, England |
| Career | Environmental Scientist |
| Professional Experience | 20 years in ecological research |
| Notable Achievements | Published multiple papers on interspecific competition |
| Reference Website | National Geographic |
In ecosystems, competition among organisms serves as a driving force behind evolutionary processes. Animals compete fiercely for food, water, and living space, leading to adaptations that enhance survival chances. Similarly, plants engage in competitive interactions, striving for optimal light exposure necessary for photosynthesis. These competitions often result in niche differentiation, where species occupy distinct roles within their environment, reducing direct rivalry over identical resources.
However, when two species share the same niche, intense competition ensues, potentially resulting in one species' dominance or extinction. Such scenarios exemplify the principle of competitive exclusion, highlighting the importance of resource partitioning in maintaining biodiversity. Moreover, invasive species pose significant threats to native wildlife by outcompeting them for vital resources, disrupting established ecological balances.
Nature's competitive landscape mirrors societal challenges faced by humans. Just as organisms fight for survival, people encounter analogous situations daily, particularly concerning accessibility issues related to service animals. Under ADA provisions, establishments must accommodate service animals unless doing so fundamentally alters operations or poses undue hardship. Consequently, businesses operating salad bars or similar self-service food lines must permit service animals' presence, aligning with legal obligations promoting inclusivity.
The interplay between competition and cooperation shapes both natural and artificial systems. While competition drives innovation and efficiency, excessive rivalry may lead to detrimental outcomes. Therefore, fostering environments conducive to collaboration remains paramount. In practical terms, this translates to designing inclusive spaces accommodating diverse needs, including those necessitating assistance from service animals.
Ecosystems worldwide face mounting pressures due to increasing competition for limited resources. Human activities exacerbate these pressures, contributing to habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Addressing these issues requires concerted efforts integrating scientific knowledge with policy implementation. By studying interspecific competition and its implications, researchers gain valuable insights applicable to conservation strategies aimed at preserving Earth's rich biodiversity.
Furthermore, understanding competition dynamics aids in managing invasive species effectively. These non-native invaders often possess traits enabling them to dominate native populations, altering ecosystem structures and functions. Successful management entails early detection, rapid response, and sustained control measures tailored to specific contexts. Public awareness campaigns play critical roles in mitigating impacts associated with invasive species invasions.
Returning to the realm of human interaction, harmonious coexistence amidst diversity necessitates robust frameworks supporting equitable treatment. ADA regulations exemplify such frameworks, mandating reasonable accommodations for individuals utilizing service animals. Institutions adhering to these principles foster inclusive atmospheres benefiting everyone involved. Simultaneously, they uphold ethical responsibilities towards ensuring fair treatment regardless of personal circumstances.
Ultimately, whether examining natural ecosystems or constructed settings, recognizing the significance of competition proves indispensable. It informs our comprehension of complex relationships governing life on Earth while guiding decisions impacting societal progress. As stewards of this planet, embracing balanced approaches encompassing competition and cooperation propels us toward sustainable futures benefitting all forms of life.
In conclusion, the nexus of competition and cooperation permeates every facet of existence. From microscopic organisms battling for nutrients to global enterprises vying for market shares, this duality influences outcomes profoundly. Leveraging lessons learned from observing natural systems enables us to craft solutions addressing contemporary challenges more effectively. Thus, cultivating awareness regarding these fundamental forces empowers us to navigate an increasingly interconnected world successfully.