Is kombucha tea truly the elixir of health that many claim it to be? This ancient fermented beverage has captured global attention for its purported benefits, yet its scientific validation remains a topic of debate. As we delve into the intricacies of kombucha's microbiology and composition, one cannot help but wonder whether this fizzy drink lives up to its reputation. From aiding digestion to boosting immunity, kombucha’s potential advantages have sparked curiosity among health enthusiasts worldwide.
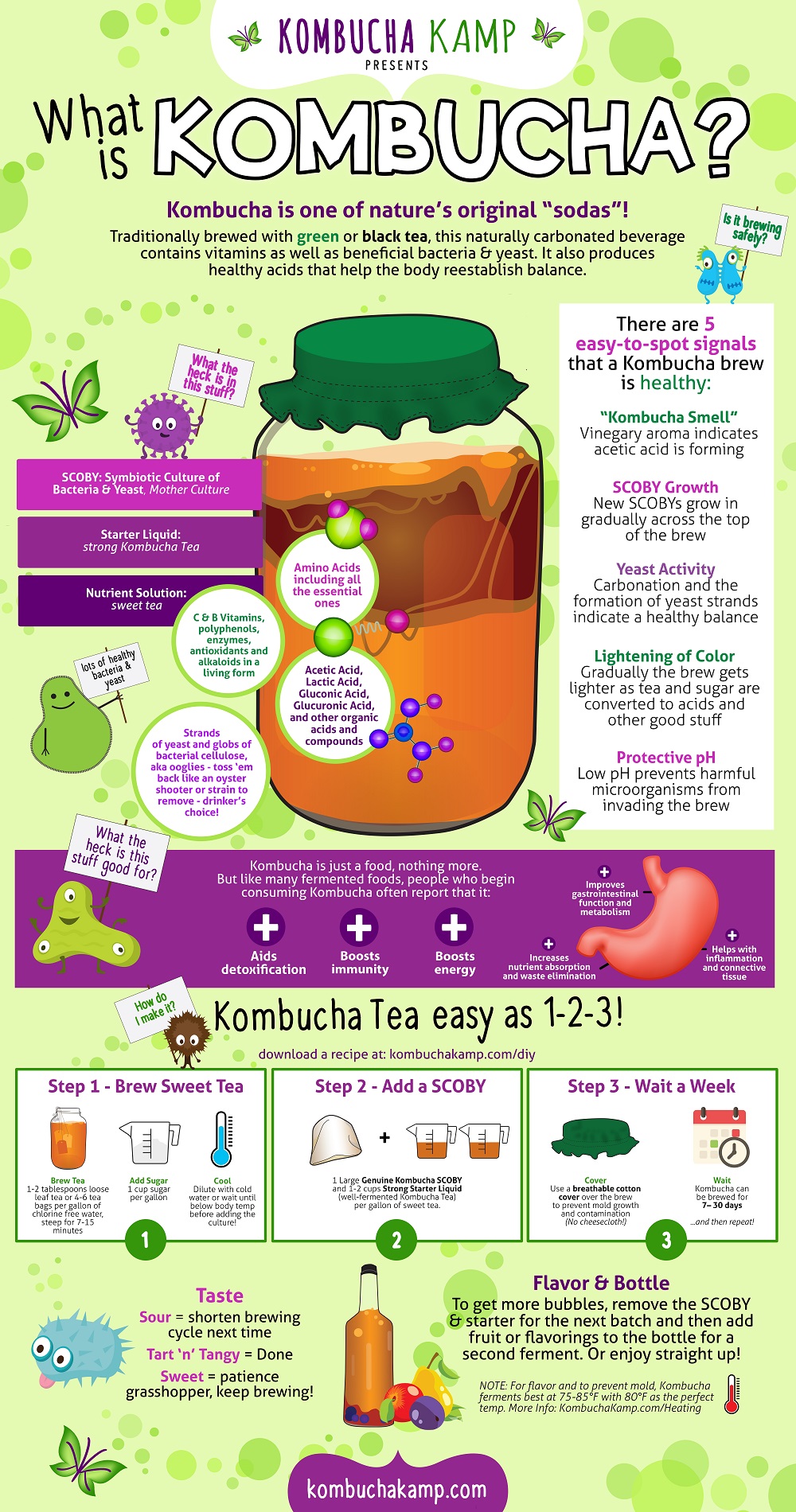
Kombucha tea is crafted through the fermentation of sugared tea using a symbiotic culture of acetic acid bacteria and yeast, often referred to as the tea fungus. This process yields a tangy, effervescent beverage rich in probiotics, organic acids, and antioxidants. Proponents argue that kombucha can enhance gut health, reduce inflammation, and even support weight management. However, sceptics caution against exaggerated claims, urging consumers to approach kombucha with a balanced perspective. The beverage's rising popularity, particularly among millennials, has fuelled an industry worth billions, with brands like Health-Ade and GT’s leading the charge.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Kombucha Tea |
| Origin | Eastern Europe and Asia |
| Key Ingredients | Sweetened black or green tea, SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture Of Bacteria and Yeast) |
| Primary Benefits | Gut health improvement, immune system support, antioxidant properties |
| Notable Brands | Health-Ade, GT’s, Spring Branch Kombucha |
| Reference Website | Health-Ade Official Site |
Despite its growing acclaim, the science behind kombucha remains inconclusive. While some studies suggest that the drink may indeed promote digestive health due to its probiotic content, others highlight concerns about contamination during home brewing. For instance, improper fermentation conditions could lead to the presence of harmful microorganisms. Moreover, individuals with compromised immune systems or specific allergies should exercise caution when consuming kombucha. Ethanol levels in certain batches might also exceed safe limits if not monitored carefully.
The microbial diversity within kombucha plays a crucial role in determining its nutritional profile. Sequence-based analyses reveal a complex ecosystem comprising various strains of bacteria and fungi. Gluconacetobacter xylinus, one of the predominant bacterial species found in kombucha, contributes significantly to the production of gluconic acid, which imparts the beverage's characteristic sour taste. Meanwhile, yeasts such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae facilitate ethanol formation during fermentation. These interactions create a unique blend of compounds believed to confer health benefits.
Prominent brands like GT’s take pride in their commitment to purity and authenticity. By adhering to traditional methods and utilising high-quality ingredients, they aim to preserve kombucha's natural essence while enhancing its flavour profiles. Their offerings span a wide array of options, including adaptogenic teas infused with herbs known for their stress-relieving properties. Similarly, Spring Branch Kombucha distinguishes itself by crafting small-batch, handcrafted brews sourced from fair-trade organic teas, ensuring both sustainability and excellence.
In addition to its potential health perks, kombucha appeals to those seeking alternatives to sugary soft drinks. With lower sugar content compared to conventional sodas, it provides a refreshing option without compromising on taste. Furthermore, its carbonation mimics the satisfying fizziness associated with popular beverages, making it an attractive choice for health-conscious consumers. Brands like Health-Ade further capitalise on this trend by emphasising their products' organic certification and absence of artificial additives.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that individual responses to kombucha vary widely. Factors such as personal tolerance, existing medical conditions, and dietary preferences all influence how one reacts to this beverage. Some users report noticeable improvements in energy levels and digestion after incorporating kombucha into their routine, whereas others experience no discernible effects. As always, moderation remains key; excessive consumption could potentially disrupt gut flora balance or exacerbate pre-existing issues.
Looking ahead, advancements in biotechnology may unlock new insights regarding kombucha's mechanisms of action. Researchers continue to explore its potential applications beyond general wellness, such as combating chronic diseases or optimising athletic performance. Nevertheless, until more comprehensive studies emerge, consumers must rely on anecdotal evidence alongside professional guidance when deciding whether to integrate kombucha into their lifestyles.
Ultimately, kombucha represents far more than just another trendy drink—it embodies a cultural phenomenon rooted in centuries-old traditions. Its resurgence in modern times reflects society's increasing focus on holistic approaches to health and wellbeing. Whether viewed as a panacea or simply a delightful treat, there is no denying that kombucha continues to captivate audiences across continents, inspiring countless stories of transformation along the way.