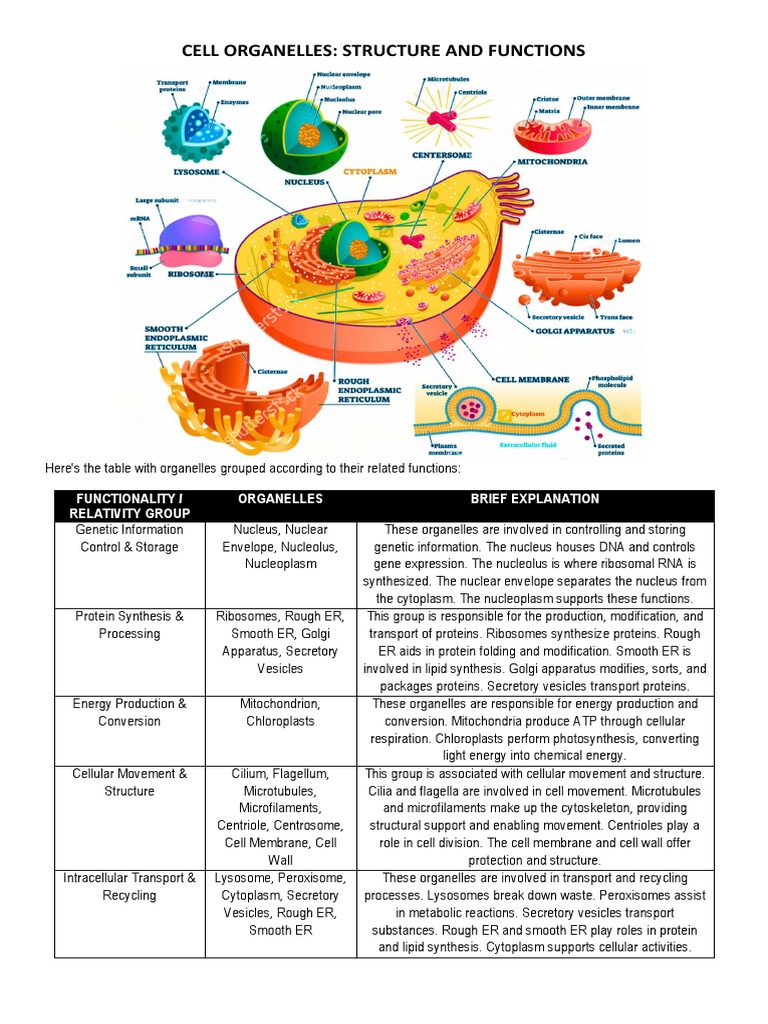
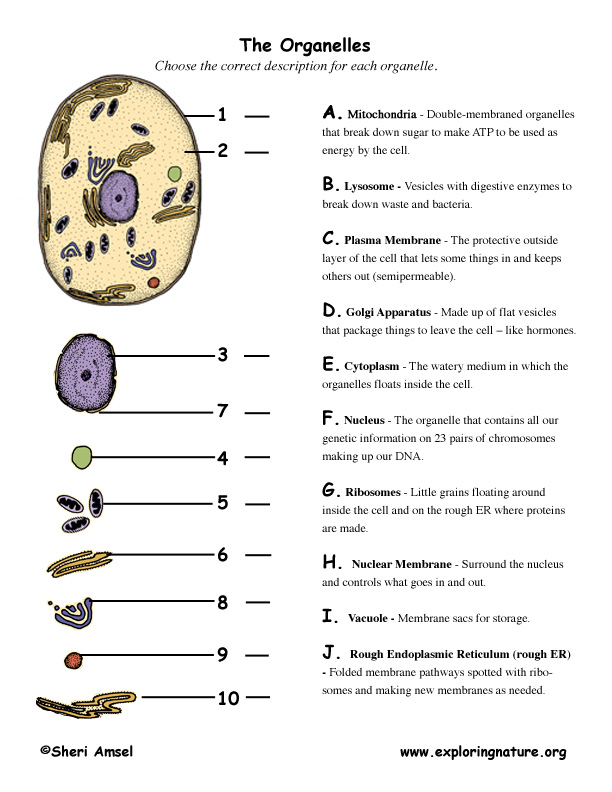
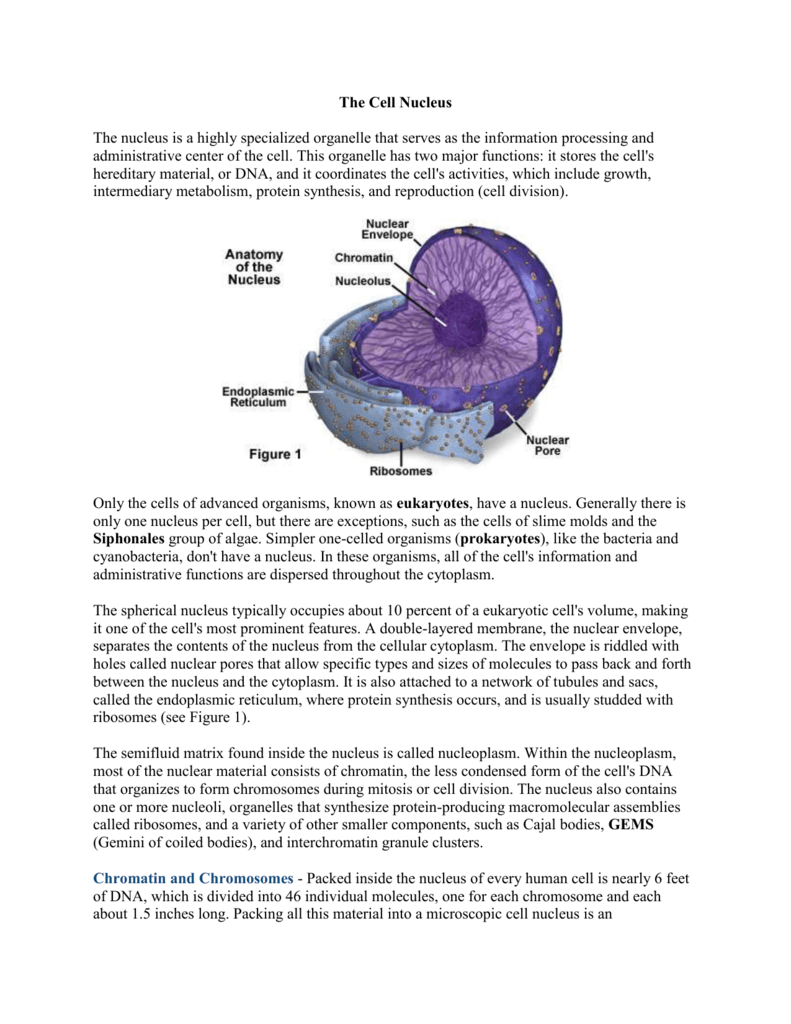
What exactly are algae, and why do they hold such significance in the study of alternative fuels? Algae represent a diverse group of eukaryotic organisms, each cell containing a nucleus and various organelles enclosed within membranes. These tiny yet powerful organisms have captured the attention of scientists worldwide as potential sources for biofuel production. The complexity of their cellular structure makes them not only fascinating but also crucial players in addressing global energy challenges.
Eukaryotes, including algae, differ significantly from prokaryotes. While prokaryotes are single-celled organisms lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, eukaryotes possess intricate internal structures that enhance their functionality. This distinction is pivotal when examining how different organisms interact with their environment and contribute to ecological processes. For instance, algae's ability to perform photosynthesis efficiently stems from their well-defined cellular architecture, particularly the presence of chloroplasts—an essential organelle responsible for capturing sunlight.
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Name | Algae |
| Type | Eukaryotic Organism |
| Cell Structure | Contain nucleus and membrane-bound organelles |
| Key Features | Photosynthetic capability, diverse species |
| Applications | Biofuel production, environmental remediation |
| Reference | EGEE 439: Alternative Fuels From Biomass |
The evolutionary journey of eukaryotes has been marked by significant milestones. Over billions of years, these organisms developed complex cellular mechanisms enabling them to thrive across diverse environments. Mitochondria, another critical organelle found in eukaryotic cells, plays a vital role in energy production through cellular respiration. This dual capability—photosynthesis in chloroplasts and energy generation in mitochondria—positions algae uniquely among living organisms. Their adaptability allows them to survive in aquatic ecosystems ranging from freshwater ponds to deep ocean floors.
In contrast, prokaryotes lack these specialized compartments, relying instead on simpler metabolic pathways. Despite their simplicity, prokaryotes remain indispensable components of Earth's biosphere. They participate actively in nutrient cycles, decomposing organic matter and recycling elements back into the ecosystem. However, their absence of membrane-bound organelles limits their capacity for certain biochemical reactions compared to eukaryotes like algae.
Paleobiologist Susannah Porter's research sheds light on ancient microbial interactions predating modern life forms. Evidence suggests predation existed even among primitive prokaryotic communities over 740 million years ago. Such findings underscore the interconnectedness of all life forms throughout history. Understanding these early relationships provides valuable insights into current biological dynamics, reinforcing the importance of studying both prokaryotes and eukaryotes together.
As humanity grapples with climate change and dwindling fossil fuel reserves, algae emerge as promising alternatives. Their rapid growth rates combined with high lipid content make them ideal candidates for biodiesel production. Moreover, cultivating algae does not compete with agricultural land use, offering sustainable solutions without compromising food security. Researchers continue exploring ways to optimize cultivation techniques and extraction methods to maximize yields while minimizing costs.
Despite advances, challenges persist. Scaling up production remains economically unfeasible due to high operational expenses and technological limitations. Additionally, ensuring consistent quality control poses difficulties given the variability inherent in natural systems. Nevertheless, ongoing innovations promise breakthroughs capable of overcoming these hurdles. Collaborative efforts spanning academia, industry, and government sectors drive progress toward realizing algae-based energy futures.
Beyond biofuels, algae offer numerous other applications. Environmental remediation represents one area where their capabilities shine brightly. Certain species effectively remove pollutants from wastewater, providing cost-effective treatment options for municipalities and industries alike. Others serve as dietary supplements rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants beneficial to human health. Furthermore, cosmetic manufacturers incorporate algae extracts into products enhancing skin hydration and elasticity.
Understanding the fundamental differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes enhances our appreciation for the complexity underlying life itself. Each category contributes uniquely to maintaining ecological balance, supporting diverse life forms, and driving evolutionary advancements. By leveraging knowledge gained from studying these organisms, we can develop innovative strategies addressing pressing global issues while fostering sustainable development practices.
Future research directions focus on unraveling genetic mysteries governing algal physiology and behavior. Advances in genomics enable scientists to identify genes responsible for desirable traits, paving the way for targeted breeding programs aimed at improving performance characteristics. Synthetic biology approaches further expand possibilities by allowing engineers to design custom organisms tailored specifically for targeted purposes.
Ultimately, algae exemplify nature's ingenuity, combining simplicity with sophistication to deliver remarkable results. As stewards of this planet, it behooves us to harness their potential responsibly, balancing exploitation with conservation. Through continued exploration and collaboration, we stand poised to unlock new frontiers in science, technology, and beyond, inspired by the humble yet extraordinary world of algae.